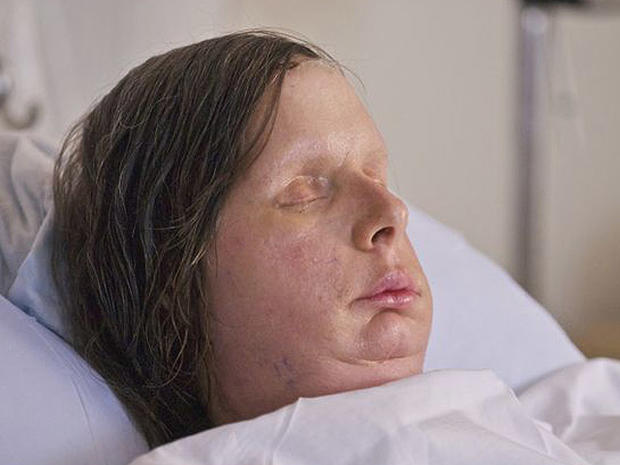
Chimp Attack Victim Back In Boston Hospital As Body Rejects Face Transplant
HARTFORD, Conn. (AP) — The Connecticut woman who underwent a face transplant five years ago after being attacked by a chimpanzee is back in a Boston hospital after doctors discovered her body is rejecting the transplant.
Read: Five Years After Chimp Attack, Victim Helps Boston Doctors Study Treatments
Charla Nash had been taking part in an experiment in which doctors at Boston's Brigham and Women's Hospital had tried to wean her off the anti-rejection drugs she had been taking since the 2011 operation.
Her doctors now hope to reverse the rejection by ending the experiment, Nash's publicist, Shelly Sindland, said.
Anti-rejection drugs can have serious side effects, and the military funded the experiment in the hopes the alternative treatment could help those needing transplants after returning from war.
"I gave it my all and know my participation in the study will still be beneficial," Nash said in a statement to The Associated Press. "I'd do it all over again, if I could. The men and women serving our country are the true heroes."
DOCTORS HOPEFUL
Nash recently discovered several unusual patches on her face, Sindland said. Doctors on Monday did a biopsy and determined her body was rejecting the transplant, she said.
Sindland said Nash told her the doctors are hopeful they can reverse the rejection by ending the experiment and putting her back on her original medication. If that attempt is unsuccessful, it isn't immediately clear what the next step would be, Sindland said.
Nash's doctors and the hospital, where Nash is expected to remain at least through the weekend, did not immediately return calls and emails Wednesday seeking comment.
The immunosuppression drugs that transplant patients are typically given for the rest of their lives carry such risks as cancer, viral infections and kidney damage. Because of those dangers, many transplants of non-vital body parts, such as thumbs, are not considered worth doing. But doctors say that could change if the drugs don't have to be a lifelong commitment.
"JUST HAPPY I HAD THE CHANCE TO HELP"
The Pentagon, which also paid for Nash's transplant, has provided grants to 14 medical facilities across the U.S. through its hand and face transplantation program. The face and the extremities are the most frequently injured parts of the body in war.
"I'm just happy I had the chance to help," Nash said. "I wish I could have done more. I believe in the power of prayer and appreciate everyone who is praying for me."
Nash lost her nose, lips, eyelids and hands when she was mauled in 2009 by her employer's 200-pound pet chimpanzee in Stamford, Connecticut. Doctors also had to remove her eyes because of a disease transmitted by the chimp.
She later received new facial features taken from a dead woman. She also underwent a double hand transplant, but it failed when her body rejected the tissue.
When she began the experiment involving the suspension of anti-rejection drugs in March, 2015, doctors said it would eventually include other patients and its findings could potentially affect hundreds of thousands of people, military and civilian alike.
Copyright 2016 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.